Breast Cancer Radiation Therapy Treatment
Radiation therapy, also known as radiotherapy, is often a part of the breast cancer treatment plan.
Radiation therapy, also known as radiotherapy, is often a part of the breast cancer treatment plan.
For the most part, surrounding healthy tissue is spared. Radiation is most commonly used after a breast-conserving surgery (also referred to as a lumpectomy) to reduce the likelihood of the cancer returning.
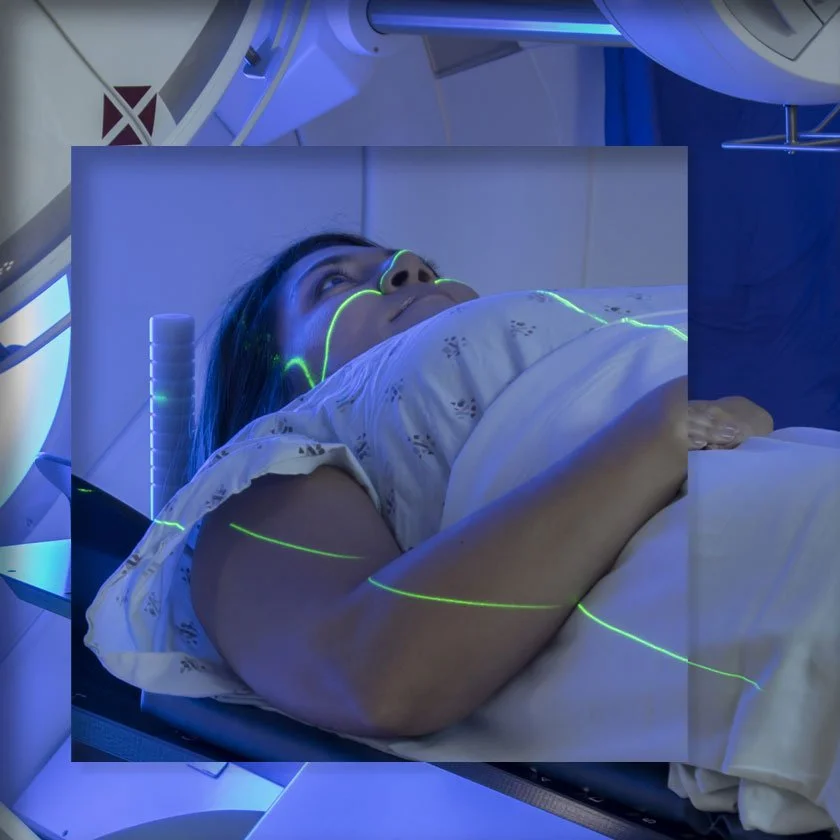
At NorthMain Radiation Oncology, you may receive one or more of the following radiation therapies to treat breast cancer:

External Beam Radiation Therapy, including Hypofractionated Radiation Therapy

This is the most common type of radiation therapy for breast cancer. External radiation therapy uses a machine outside the body, called a linear accelerator, to send radiation beams toward the area of the breast where the cancer was located. Depending on your situation, radiation may be administered to the whole breast or just the area of the breast affected by the cancer (partial breast radiation). This type of treatment is meant to kill any cancer cells left behind after surgery that couldn’t be detected with the naked eye. Some patients will also receive chemotherapy or other breast cancer treatments. Sometimes radiation therapy for breast cancer patients is given over the course of the same weeks as chemotherapy. And for other patients one type of breast cancer treatment may be followed by another.
Radiation therapy is typically administered five days a week for a period of 6 to 8 weeks. Recently a new approach is used called hypofractionated radiation therapy. With this method, the patient receives their full dose of radiation in a shorter time period. Instead of a 6-8 week course of radiation therapy, the same results can be achieved in 4-5 weeks. This is done by giving a higher dose of radiation at each treatment. The higher dose has been proven safe and effective for many breast cancer patients.
Our radiation oncologists will work with the breast surgeon and the medical oncologist to determine the right timing of external beam radiation therapy for you.

Internal radiation therapy means that a radioactive substance used to kill cancer is placed in the body for a period of time. In the case of breast cancer, the process of internal radiation therapy typically lasts a few days.
HDR brachytherapy delivers radiation to the lumpectomy location by placing an applicator tube into the breast temporarily. Once the applicator is in place, small radioactive ribbons, or pellets are placed in the applicator to deliver radiation inside of the breast.
The exact length of time for the treatment is recommended for each patient based on the size of the surgery site and the stage of breast cancer. For some patients, the radiation may be left in for a few consecutive days. For others, it could be left in for several minutes at a time, repeating over the course of a week or so.
Would you like to learn more about whether this is an option for you?
Accelerated Partial Breast Irradiation (APBI) is an approach that treats only the lumpectomy cavity plus a 1-2 cm margin, rather than the whole breast. Because of this, a higher dose can be delivered in a shorter (accelerated) period of time. APBI may be an option for patients with early-stage breast cancer.
There are various types of accelerated partial-breast radiation, which include:
3-D conformal radiation therapy (3DCRT): Uses a computer to shape the radiation beams to fit the tumor. Radiation treatments are done once or twice a day for 1 week.
Multicatheter interstitial brachytherapy: The use of tiny catheters to deliver radioactive seeds. Seeds may be left in the tubes for a few hours or a few days, and you remain in the hospital during treatment.
Balloon catheter brachytherapy: The use of a special tube with a balloon on one end to deliver a radioactive seed. This is usually done as an outpatient procedure with a total of 10 treatments given over a 5-day period.
Intraoperative radiation therapy (IORT): An intensive radiation treatment that's administered during surgery.
Side effects from radiation treatment can vary, but there are some common side effects to watch for and talk to your oncologist and radiation technician who you will see often. They can often help you with treating the side effects and minimizing their effects.
Common side effects of radiation for breast cancer include:
Fatigue
Tenderness to the touch, especially at treatment site
Red, dry, tender, or itchy skin similar to a sunburn
Swelling, which may feel like breast “heaviness”
You have a choice where you receive radiation therapy. NorthMain Radiation Oncology offers patients the latest radiation therapies for cancer treatment close to home. Since you will visit the radiation therapy clinic often, it's important to choose not only a radiation oncologist you trust but also a convenient location. If you live in the Providence area and are seeking radiation therapy for cancer treatment, click the button below to request an appointment.